Available with Spatial Analyst license.
Summary
Performs a Boolean And operation on the cell values of two input rasters.
Illustration
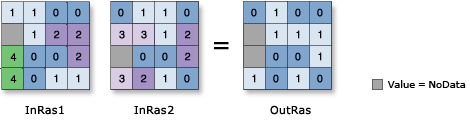
Discussion
The & operator will perform a Boolean And operation when one or more input (operand) is a raster. If both inputs (operands) are numbers, then the & operator will perform Bitwise And operation. For more information on how to work with operators, see Working with operators.
When multiple operators are used in an expression, they are not necessarily executed in left-to-right order. The operator with the highest precedence value will be executed first. For more information on operator precedence, see operator precedence table. You can use parentheses to control the execution order.
Boolean (~, &, ^, |) operators have a higher precedence level than Relational (<, <=, >, >=, ==, !=) operators. Therefore, when Boolean operators are used in the same expression as Relational operators, the Boolean operators will be executed first. To change the order of execution, use parentheses.
When multiple Relational and/or Boolean operators are used consecutively in a single expression, in some cases it may fail to execute. To avoid this potential problem, use appropriate parentheses in the expression so that the execution order of the operators is explicitly defined. For more information, see Complex Statement Rules.
Two inputs are necessary for the Boolean evaluation to take place.
The order of input is irrelevant for this operator.
If the input values are floating point, they are converted to integer values by truncation before the Boolean operation is performed. The output values are always integer.
Another way to perform the Boolean And operation is a &= b which is an alternative way to write a = a & b.
Syntax
in_raster_or_constant1 & in_raster_or_constant2
| Operand | Explanation | Data Type |
in_raster_or_constant1 | The first input to use in the Boolean And operation. If one of the inputs is a raster and the other is a scalar, an output raster is created with the evaluation being performed for each cell in the input raster. | Raster Layer | Constant |
in_raster_or_constant2 | The second input to use in the Boolean And operation. If one of the inputs is a raster and the other is a scalar, an output raster is created with the evaluation being performed for each cell in the input raster. | Raster Layer | Constant |
Return Value
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| out_raster | The output raster object. The output values will be either 0 or 1. | Raster |
Code sample
This sample performs a Boolean And operation on two input rasters.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
outBooleanAnd = Raster("degs") & Raster("negs")
outBooleanAnd.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outbooland.img")This sample performs a Boolean And operation on two input rasters.
# Name: Op_BooleanAnd_Ex_02.py
# Description: Performs a Boolean And operation on the cell values
# of two input rasters
# Requirements: Spatial Analyst Extension
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
from arcpy.sa import *
# Set environment settings
env.workspace = "C:/sapyexamples/data"
# Set local variables
inRaster1 = Raster("degs")
inRaster2 = Raster("negs")
# Check out the ArcGIS Spatial Analyst extension license
arcpy.CheckOutExtension("Spatial")
# Execute BooleanAnd
outBooleanAnd = inRaster1 & inRaster2
# Save the output
outBooleanAnd.save("C:/sapyexamples/output/outbooland")